In the vast business landscape, companies use various metrics to calculate the efficiency of their business and how they manage their inventories to convert them into cash.
Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO), is the number of days the Inventory remains and how many times it takes to sell in the market, showing the efficiency of the company and how effectively it manages its inventory. It is basically a financial metric that indicates the average number of days a company takes to sell its products and services to cash during a given period, increasing its revenue.
So, let’s break down the core concept of the days inventory outstanding for any business.
What is Days Inventory Outstanding
Days Inventory Outstanding is the financial metric used to measure the flow of the inventory and how much time it takes to convert into cash, generating revenues. The higher the inventory, means higher the maintenance cost, which increases the price of the product or services. Today, businesses focus on reducing the number of inventories, resulting in a low price for holding costs. To reduce the maintenance cost of the inventory, businesses continue to keep specs on their inventory stock to cover the fluctuating demands of their products in the market. The lower the dio meaning, the higher the turnover, reflecting the efficient inventory management of the company.
In other words, inventory turnover reflects the flow of inventory, which is the measurement of the conversion of inventory into cash.
A high Days Inventory Outstanding means the company has too much inventory, raising the inventory maintenance costs that involve warehouse space, holding costs, and wastage of product and the stock obsolescence. Therefore, by assessing the demand of the product and matching sales with stockholding, inventory managers can manage their inventories efficiently.
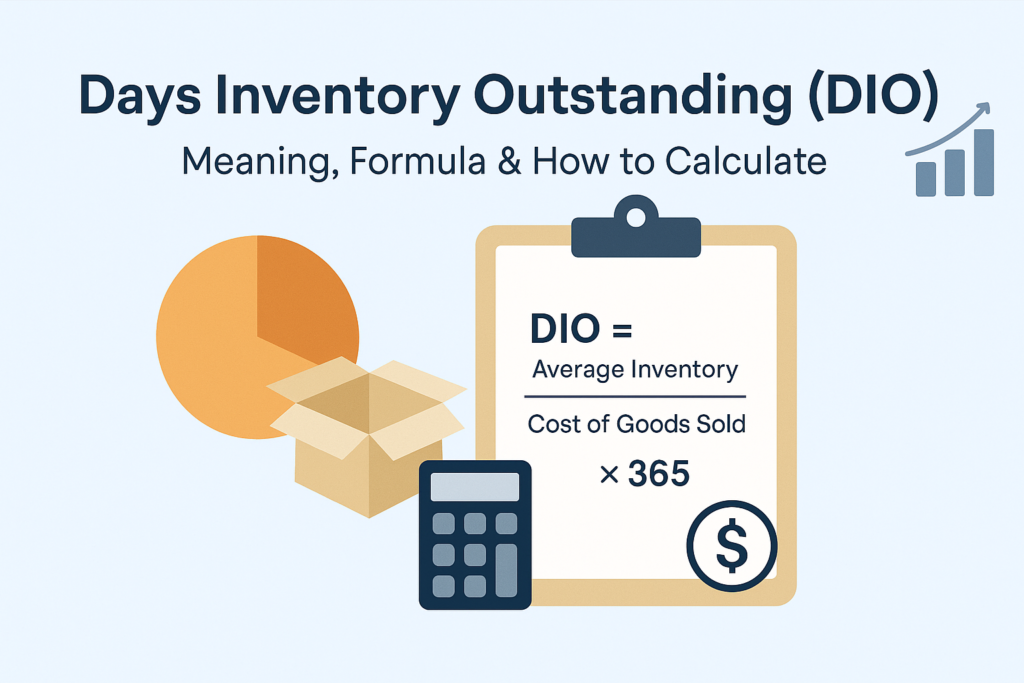
How to Calculate DIO
Using the following days in inventory formula, you can calculate DIO. Here is how.
- The Days Inventory Outstanding formula is
DIO = (Average inventory/COGS) x number of days
- To calculate average inventory
Average inventory = (Opening Inventory + Closing Inventory)/2
However, some companies use a weighted average to calculate the Days Inventory Outstanding, which requires a more complex formula.
COGS means the cost of buying or producing the product. It can be fetched from the income statement of the entity.
The number of days’ sales in inventory depends on the period you measure. For one year, DIO, is divided by 365 days, while for quarters divided by 90 days, and 30 days for a monthly DIO calculation.
Components to Calculate Days Inventory Outstanding
- Inventory Balance: To calculate the Days Inventory outstanding, it requires the inventory items that represent the value of the raw materials, work-in-progress goods (WIP), and finished goods of a company mentioned in the balance sheet of the company.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The COGS line items of a company represents the direct costs incurred by a company while selling its goods or services to generate revenue that is mentioned on the income statement of the entity.
By utilising the above formula, Days Inventory Outstanding can be calculated easily, helping managers to make strategies accordingly.